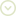Cicada Killer Wasps

These large (1-1/3- to 1-5/8-inch long) wasps fly slowly above the ground. Cicada killers have a black body with yellow marks across the thorax and abdomen. Wings are reddish-orange.
Although these wasps are huge, they usually ignore people. Males may act aggressively if they are threatened, but are unable to sting. Females can sting, but are so passive that they rarely do. Even if they do sting, the pain is less than that of smaller wasps such as the yellow jacket or paper wasp and is similar to the sting of a sweat bee.
The cicada killer is a solitary wasp rather than a social wasp like the yellow jacket. The female nests in burrows in the ground. These burrows are quarter-size in diameter and can go 6 inches straight down and another 6 inches horizontally. Adults normally live 60 to 75 days from mid-July to mid-September and feed on flower nectar and sap. The adult female seeks cicadas on the trunks and lower limbs of trees. She stings her prey, flips it over, straddles it and carries it to her burrow. If she has a tree to climb, she will climb the tree so she can get airborne and fly with cicada back to the nest. If not, she will drag it. She will lay one egg per cicada if the egg is left unfertilized. Unfertilized eggs develop into males only. Fertilized eggs develop into females and are given at least two cicadas. Cicadas are then stuffed into the female’s burrow. Each burrow normally has three to four cells with one to two cicadas in each. However, it is possible for one burrow to have 10 to 20 cells.
Eggs hatch in two to three days, and larvae begin feeding on paralyzed cicadas. Feeding continues for four to 10 days until only the outer shell of the cicada remains. The larva overwinters inside a silken case. Pupation occurs in the spring. There is one generation per year. Cicada killers are not dangerous, but they can be a nuisance. If you believe control is necessary, treat the burrows after dark to ensure the female wasps are in their nests. The males normally roost on plants near burrow sites. They can be captured with an insect net or knocked out of the air with a tennis racket during the day.
http://hnr.k-state.edu/extension/info-center/newsletters/index.html
-
March 2, 2024
Firefighters rush to subdue deadly Panhandle wildfire before dangerous conditions return Saturday -
February 14, 2024
Texas Workforce Commission presents Texas Conference for Employers -
February 1, 2023
Are your trees damaged by the ice storm? -
July 28, 2022
Another benefit of Texas trees: Cooler temperatures -
February 25, 2022
Time to Plant Trees in Texas -
January 27, 2022
Treemergency: Mulch Volcanos are Erupting in Landscapes! -
December 21, 2021
Cedar fever season in Texas -
November 9, 2021
Texans celebrate 2021 Arbor Day in Weatherford, Texas – and beyond -
June 24, 2021
41st Texas Tree Conference, Academy, Trade Show and Tree Schools -
February 17, 2021
Texas Sized Winter Storms Can Damage Trees